Management Process:�
Step 1: Defining PR Problems�
Step 2: Planning & Programming
Dr. Iccha Basnyat
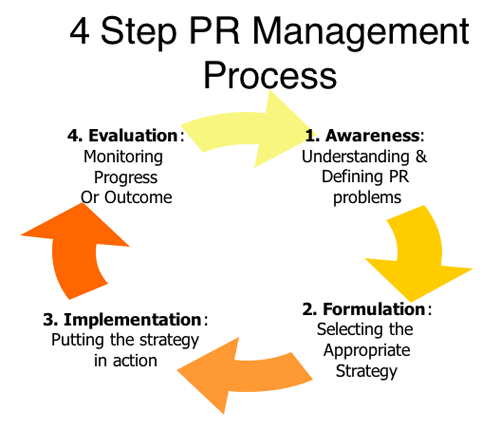
- Step 1: Problem Definition
- Problem definition >> Judgment about a situation
- Judgment >> Understanding current situation
- -- objectively & systematically
- Step 1: Understanding Current Situation
- What is the nature of the Problem/Issue?
- What has been happening that this is unsatisfactory?
- What factors seem to have caused this problem?
- What kinds of information is needed to access the situation?
- Who is affected by the problem?
- Research in PR
- Research:
- Lays the groundwork for effective PR via evidence
- Should be used in every phase of the management process
- -- Primary or Secondary Techniques
- -- Critical for problem solving and/or issue management
- -- Likelihood something will affect the organizational
objectives
- Increase credibility of the profession
- Good information - good decision making
- Helps with appropriate strategies
- What kind of information is required should help you chose
your research method
- Systematic Situational Analysis
- Internal Analysis:
- External Analysis:
- (Internal) Research in PR
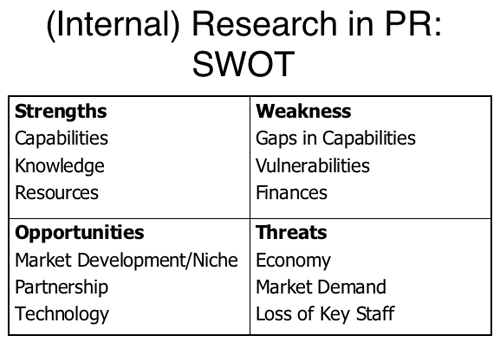
- (External) Research in PR
- Informal:
- Personal contacts
- Key Informants
- Community Forums
- Advisory Committee/Boards
- Call in/Mail Analysis/Online
- Pros/Cons:
- Formal Methods:
- Secondary Data
- Content-Analysis (quantify or meanings)
- Surveys
- Focus groups
- Interviews
- Pros/Cons:
- Research in PR
- Quantitative (survey)
- -- Interested in numbers
- -- Generalizing from sample to population
- Qualitative (Interviews)
- -- Discovering opinions, experiences, expectations
- Qualitative (Focus Groups)
- -- Often forms the basis for survey questions
- -- Pre-testing questions
- -- Market Research
- Research in PR: Discussion question:
- Company XYZ is located in a town of 500,000 people. The
company has 6,000 employees making it the largest in town.
Despite this, the management believes that the company doesn’t
have a strong identity & visibility in the community.
- You are asked to conduct research to determine exactly
what the company’s image is in the community.
- What method of research would you use? Formal? Informal?
Why?
- What kinds of information about the company’s
image should be researched?
- From Step 1 to Step 2
- Through research, at the end of step 1:
- 1. Issue Identification
- --Understood & defined the nature of the PR problem
- 2. Issue Analysis
- -- Assessed that this is important to the organization
and its publics
- Step 2: Planning & Programming
- Strategic & Systematic Approach
- -- Strategically addressing the problem about program
objectives, key publics,
- -- Strategic:
- -- Carefully planning for a desired end based on the
information collected
- -- Requires lots of information for informed strategy
(i.e. research)
- Strategy vs. Tactic
- Strategy:
- -- Overall plan of what you intend to achieve
- -- Long term direction for how in concept (broad statements)
objectives will be met
- Tactic:
- -- Activities specifically created and selected to carry
out the strategy
- -- Assess which tactic is most appropriate & can be
done (within time frame & budget)
- -- Theories can determine tactics
- Example: Strategy vs. Tactic
- Ex 1:
- Objective: Increase brand awareness to increase sales
- Strategy: Develop many story angles around the key message
OR Use media to reach prospective customers
- Tactic: Hold events, Contact all media outlets
- Ex 2:
- Objective: Publicize new product
- Strategy: Mount media relations campaign
- Tactic: Press conference, Press releases
- Step 2: Planning & Programming
- Strategic & Systematic Approach
- Systematically establishing goals and direction, i.e.
- -- What is the program objective?
- -- How will the appropriate strategy be selected?
- -- Who will be targeted?
- Systematic:
- -- Approaching the strategic planning in a structured
manner
- Strategic & Systematic Thinking
- --Who will this be targeted towards
- -- information >> campaign
- -- Often relies on a theory for campaigns
- --What might be done to solve the problem/issue?
- -- What are the relative merits of our possible solutions
(i.e. benefits and consequences of each proposed solution?)
- -- Is behavior always rational? Intentional?
- -- What about cultural influences?
- Step 2: Planning & Programming
- Strategic & Systematic Planning:
- Improves effectiveness
- Encourages long-term view
- Assists pro-activeness
- Minimises mishaps
- Allows informed decision making
- Going back to the earlier case:
- After your research you find out for a fact that there
is a negative image in the community about the organization
XYZ
- a. Come up with an objective for your plan to build
&/or restore organizational image
- b. Based on your objectives come up with possible
strategy/strategies to address your objective (of your
plan)
- c. What tactics would you utilize to achieve these
strategy/strategies
- Example:
- Issue Management
- Issues >> affect strategic direction of the
organization
- -- i.e. Internal or External Issues
- Strategic Thinking to address issues
- -- Pretesting of ideas, strategy, tactics, messages
- Strategic Issue Management
- Issue Management:
- Ability to direct all strategies towards achievement of
objectives
- Strategic planning beforehand
- Research >> Identification & Tracking of issues
- Priority to respond to issue
- High: Crisis
- Medium: Risk
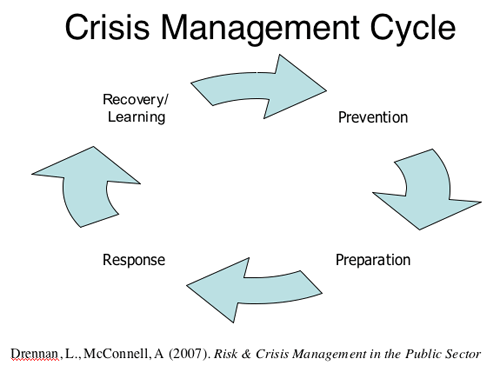
- Crisis Management
- Issue vs. Crisis
- -- Unmanaged issues turn into crisis
- -- Issue management (proactive & strategic planning)
- Crisis: Actual vs. Perception
- -- Think (i.e. public)
- -- Expectation (i.e. public)
- -- Exxon
- -- Lucozade
- Crisis
- Immediate crisis:
- Unexpected, little time for research & planning (i.e.
reactive)
- Emerging crisis:
- Allows time for research & planning >> corrective
action before reaching critical stage (i.e. proactive)
- Sustained crisis:
- Remains overtime (i.e. speculation)
- Strategic Crisis Management
- Coco-Cola’s Dasani Crisis:
- -- Clear focused objective
- To protect the global reputation of Coke-Cola
- -- Came up with appropriate strategy to deal with
issue
- -- Avoid media speculation
- -- Acted Quickly w/following tactics
- -- Narrowed down the issue to specific mineral
- -- Conducted media interviews\
-
-- Incident Management and Crisis
Resolution Team
- Risk vs. Crisis
- Risk:
- Something that can affect the outcome of the organizational
objective
- i.e. Launching new product
- Anticipating, minimizing & preventing loss
- i.e. Informing public of risk
- Mad cow disease (UK Beef)
- SARS
Back to top |
